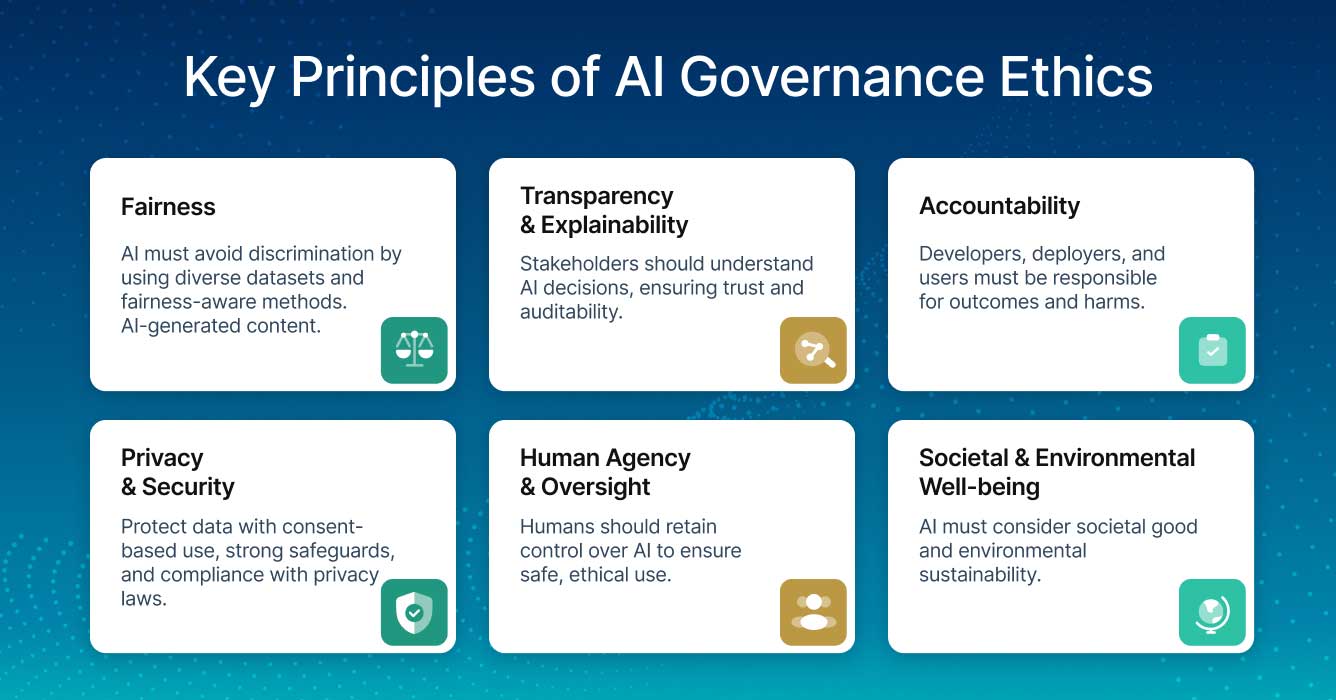
The rapid integration of artificial intelligence into critical infrastructure has fundamentally shifted the conversation around technology. It is no longer sufficient to ask if a system can perform a task; organizations must now determine if it should. This distinction lies at the heart of the relationship between ai ethics and governance.
For AI developers, healthcare executives, and compliance professionals, the challenge is operationalizing abstract ethical principles into concrete engineering constraints. Governance provides the scaffolding that transforms vague notions of “fairness” or “safety” into auditable, enforceable protocols. Without this structure, the deployment of advanced models introduces unacceptable levels of legal, reputational, and societal risk.
Build Trust in Artificial Intelligence With Ethical Governance Frameworks
Trust is the primary currency for AI adoption. Stakeholders—whether they are patients, regulators, or consumers—will not engage with systems they perceive as opaque or unsafe. Organizations gain this trust not through marketing, but by implementing structured governance frameworks that enforce ethical standards across the entire AI lifecycle, from initial data collection to final deployment.
Ethical ai organizations recognize that governance is not a bottleneck, but a mechanism for assurance. By establishing clear protocols for data lineage, bias detection, and model validation, companies demonstrate that their systems are under control. This rigor ensures that ethics in ai moves beyond theoretical discussions and becomes a measurable standard of performance.
To maintain this standard, forward-thinking enterprises often anchor their programs in comprehensive AI Governance Policies that map directly to global regulations and safety standards, ensuring that every development team operates from a unified source of truth.
Strengthen Organizational Resilience Through Responsible AI Oversight
In regulated industries like healthcare and finance, resilience is defined by the ability to withstand scrutiny and prevent failure. Ethical use of ai creates a defensive layer against operational shocks. By enforcing internal checks and maintaining strict auditability, oversight reduces the accumulation of “governance debt”—the hidden risk that piles up when models are deployed without documentation or safety rails.
The intersection of ai and ethics is where risk management occurs. An organization may draft a high-level ai code of ethics, but without oversight mechanisms to enforce it, the code remains a dormant document. True resilience comes from the ability to prove, at any moment, that a specific decision made by an algorithm adhered to the organization’s safety protocols. This accountability is vital for maintaining operations in high-risk environments where errors can lead to significant liability. In high-stakes clinical environments, structured healthcare AI governance frameworks formalize oversight, auditability, and accountability controls to ensure that AI-driven decisions align with patient safety standards and regulatory expectations.
How Can You Align AI Strategy With Regulatory and Ethical Standards?
The regulatory landscape is becoming increasingly complex, with frameworks like the EU AI Act and the Colorado AI Act setting new baselines for compliance. Leaders must determine how to align their broader business strategy with these evolving requirements.
Successful alignment requires treating artificial intelligence ethics as a core component of the business logic, rather than an afterthought. Ai ethics organizations and standard bodies (like NIST and ISO) provide the blueprints for this alignment. By mapping internal strategies to these external standards, organizations ensure that their innovation trajectory does not veer into non-compliance. This strategic alignment reduces legal exposure while enhancing long-term competitiveness, as compliant systems are easier to scale globally than those built on shaky regulatory foundations.
Accelerate Innovation While Managing AI Risks and Accountability
There is a misconception that governance slows down development. In reality, responsible AI practices act as brakes on a high-performance car: they allow the driver to go faster with confidence. Practices such as rigorous risk assessments, human-in-the-loop design, and explainability enable continuous innovation because they preserve control over unintended outcomes.
The ethics of ai dictates that creators are responsible for their creations. This accountability is particularly challenging with the rise of generative models, which can behave unpredictably. Validating these complex systems requires specialized Testing for Generative AI that goes beyond standard performance metrics to evaluate safety, hallucination rates, and toxicity, ensuring that ethical ai remains robust even as model capabilities expand. By addressing the ethics of artificial intelligence proactively, teams can deploy cutting-edge tools without fear of reputational catastrophe.
How Can You Operationalize Ethical AI Using Scalable Governance Tools?
Principles must eventually become practices. To operationalize artificial intelligence governance, organizations require tools that scale. Manual spreadsheets and disparate emails are insufficient for managing the risks of modern machine learning pipelines.
Effective governance relies on platforms that provide model monitoring, automated ethical review workflows, and real-time auditing. These tools turn ethics in artificial intelligence into daily actions. In this context, AI governance implementation focuses on translating ethical principles and regulatory requirements into repeatable operational processes that can be consistently applied across AI systems.
For example, automated monitors can detect data drift that might introduce bias, triggering a review before the model harms consumers. This is particularly critical in sensitive sectors, such as Generative ai governance in healthcare, where patient outcomes depend on the reliability and fairness of the system.
Address Global AI Ethics Challenges With Transparent Governance
AI deployment is often global, but ethical norms and regulations are local. Analyzing global disparities in ai ethics reveals significant gaps in how data usage rights, algorithmic fairness, and human rights are protected across borders.
Transparent governance mechanisms bridge these gaps. When an organization documents its decision-making process and makes that data accessible (where appropriate), it addresses the challenges of ethical ai use head-on.
Transparency allows international stakeholders to verify that a system respects local norms and legal requirements, facilitating cross-border deployments that honor the rights of all affected populations.
Empower Teams to Build Ethical and Explainable AI Systems
Ultimately, systems are built by people. Empowering teams to build ethics in ai requires a combination of training, culture, and tooling. Collaboration between technical data scientists and legal compliance officers is essential to translate the ethics of artificial intelligence into code.
Leading ai ethics organizations foster this collaboration by providing developers with the resources they need to understand the implications of their work. Furthermore, adoption of explainability tools allows teams to look inside the “black box,” ensuring that decisions are interpretable. To facilitate this, leaders often deploy a dedicated ai compliance tool to bridge the gap between technical execution and legal obligation, ensuring that every system is both high-performing and ethically aligned.
FAQ
Q1: What is the role of AI governance in strengthening organizational resilience?
AI governance builds resilience by enforcing internal checks and auditability. It ensures that algorithmic decisions are documented and accountable, which mitigates legal, operational, and reputational risks before they escalate into crises.
Q2: How does responsible AI oversight contribute to regulatory compliance?
Responsible oversight aligns internal development workflows with external legal requirements. By maintaining continuous monitoring and documentation, organizations can prove adherence to regulations like the EU AI Act or Colorado SB24-205 during audits.
Q3: Can ethical AI practices coexist with rapid innovation?
Yes. Ethical AI practices, such as robust testing and risk assessment, enable faster innovation by providing the safety rails necessary to deploy advanced technologies with confidence, reducing the likelihood of costly rollbacks or failures.
Q4: What tools enable the operationalization of AI ethics at scale?
Operationalizing ethics requires governance platforms that automate model monitoring, risk classification, and documentation. These tools replace manual processes, allowing organizations to apply consistent ethical standards across hundreds of models simultaneously.
Q5: Why is transparency critical in addressing global AI ethics challenges?
Transparency allows organizations to demonstrate how their systems function and how decisions are made. This is vital for navigating differing global standards regarding data rights and fairness, ensuring that AI systems are accepted and trusted across international borders.


